Picture Perfect AV Systems
May 9, 2018 / General, Installation and testing, Upgrading and troubleshooting, Industrial Networks
Whether it’s video conferencing or digital signage, many of you are likely facing requests from your customers to deploy cable plants that support audio-visual systems.
Many of these applications utilize HDBaseT or IP-based video transmission, and technology advancements now make it possible to deliver power to video displays simultaneously with these video signals over the same cabling. When it comes to deploying and testing cable plants required to support these AV systems, it’s important to understand best testing practices to ensure your customers get the perfect picture they expect.
Different Protocol, Same Concerns, One Tester
HDBaseT is a consumer electronic and commercial connectivity standard for transmitting uncompressed 4K video signals, audio, 100BaseT Ethernet data, power and various control signals over common category copper cabling up to 100 meters. While this is similar to IP-based video systems, and the cabling and connectivity may look the same, the two are actually different protocols. Unlike IP-based video that runs over the data network using packet-based Ethernet via common network switches and routers, HDBaseT is not packet based and instead uses HDBaseT transmitters and receivers that are separate from the data network.

But don’t let this worry you. Since both HDBaseT and IP-based video run over the same cabling media used for data transmission, they are deployed using the same best practices and are subject to the same performance parameters. So if Category 6A cable is deployed for either HDBaseT or IP-based video, it must be certified to meet the TIA Category 6A standard – especially if you want to receive the manufacturer's warranty.
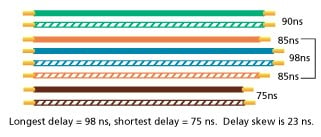
One performance parameter that matters most when it comes to achieving a perfect picture is propagation delay skew. Propagation delay (expressed in nanoseconds) is the amount of time it takes for a transmitted signal to be received at the other end of the link or channel. Propagation delay skew is propagation delay that differs from one pair to another in a four-pair twisted-pair cable. For high-resolution RGB video signals where each color is sent down a separate pair, too much delay skew can cause a jittery picture on a video displays. That’s why cabling vendors tout their “low skew” cables as ideal for video applications.
Something else common to both HDBaseT and IP-based video systems is that both can now transmit higher levels of DC power using all four pairs of a twisted-pair cable—one using power over HDBaseT (POH) and the other using power over Ethernet (PoE). POH delivers up to 100W of DC power over four pairs in conjunction with the HDBaseT video signals, while PoE delivers up to 60W (Type 3) or 90W (Type 4) of DC power over four pairs in conjunction with the IP-based video signal. These power levels are enough to power typical LED video displays, eliminating the need for AC power.
This also means that both systems come with the same concerns inherent when running higher DC power over all four pairs, such as insertion loss caused by heat rise and DC resistance unbalance caused by poor workmanship or subpar cable quality. Delivering POH or PoE is achieved by applying common-mode voltage that evenly splits the current between each conductor in the pairs, which requires DC resistance of each conductor to be equal. Difference in resistance between two conductors is DC resistance unbalance, and too much of it can cause the video signals to become distorted. With all four pairs transmitting power, DC resistance unbalance between multiple pairs also matters.
The good news is that a Fluke Networks DSX CableAnalyzer™ Series copper cable certifier will do it all to make sure your customer’s AV systems are picture perfect. Not only will it will certify cabling plants to industry standards for both HDBaseT and IP-based video deployments, including propagation delay and delay skew, but its ability to test for DC resistance unbalance can also verify the ability of the cable plant to support POH and PoE.
To learn more about testing AV systems, Read White Paper: Audio / Video (AV) Cabling Considerations