Testing Coaxial Cabling - MicroScanner2
- Coaxial: 75 Ω, 50 Ω, 93 Ω
- Length test Range: 460 m (1500 pi)
- Résolution : 0,3 m (1 pi)
- Précision type : ± 4% or 0,6 m (2 ft) whichever is greater, NVP uncertainty is an additional error.
- Étalonnage : User-settable NVP for twisted pair and coax. Peut déterminer la valeur NVP réelle avec une longueur connue du câble.
Testing Coaxial Cabling
Turn on the tester; then press PORT to switch to coaxial test mode.
Connect the tester and wiremap adapter or ID locator to the cabling as shown in Figure 1.
For cabling not terminated with an F-connector, use an adapter or hybrid patch cord to connect to the cabling.
The test runs continuously until you change modes or turn the tester off.
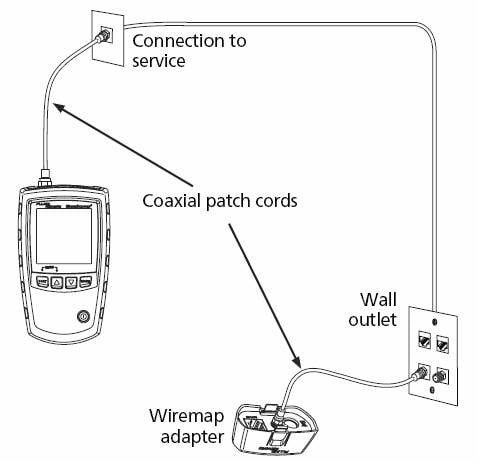
Figure 1 Connecting to Coaxial Cabling
Figure 2 shows a good coaxial cable 38,4 m long and terminated with remote ID number 3.
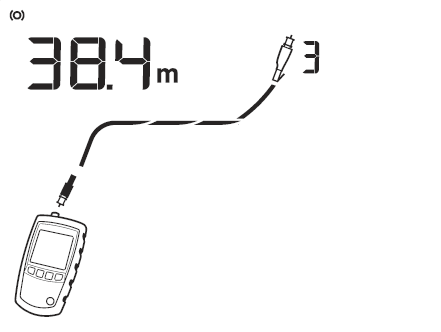
Figure 2 Coaxial Results
Open on Coaxial Cabling
Figure 3 shows an open 12,1 m from the tester.
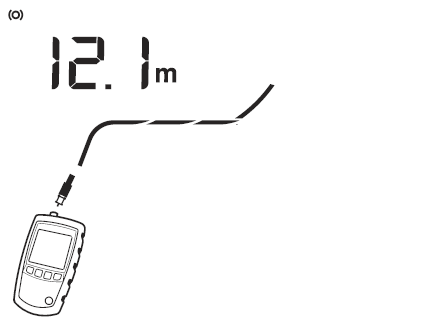
Figure 3 Open on Coaxial Cabling
Short on Coaxial Cabling
Figure 4 shows a short 12,1 m from the tester.
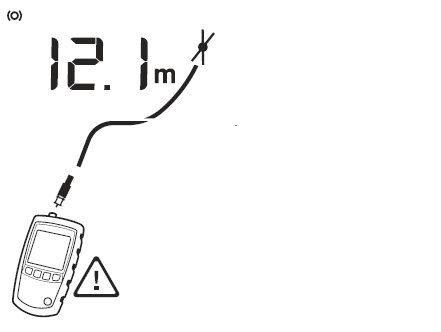
Figure 4 Short on Coaxial Cabling
Unknown Termination on Coaxial Cabling
Figure 5 shows a cable connected to a device at the far end, such as a television, CATV service, VCR, DVD player, satellite dish, splitter, or antenna. Dashes shown for length mean the tester cannot measure length because the device does not produce reflections.
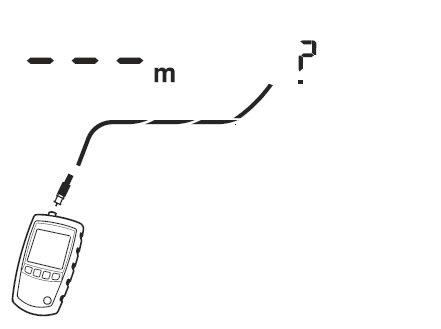
Figure 5 Unknown Termination on Coaxial Cabling
Diagnosing Wiremap Faults
Typical causes of wiremap failures:
Ouvert
- Wires connected to wrong pins at connector or punchdown blocks
- Faulty connections
- Damaged connector
- Damaged cable
- Wrong application for cable
Short
- Damaged connector
- Damaged cable
- Conductive material stuck between pins at connector.
- Improper connector termination
- Wrong application for cable




